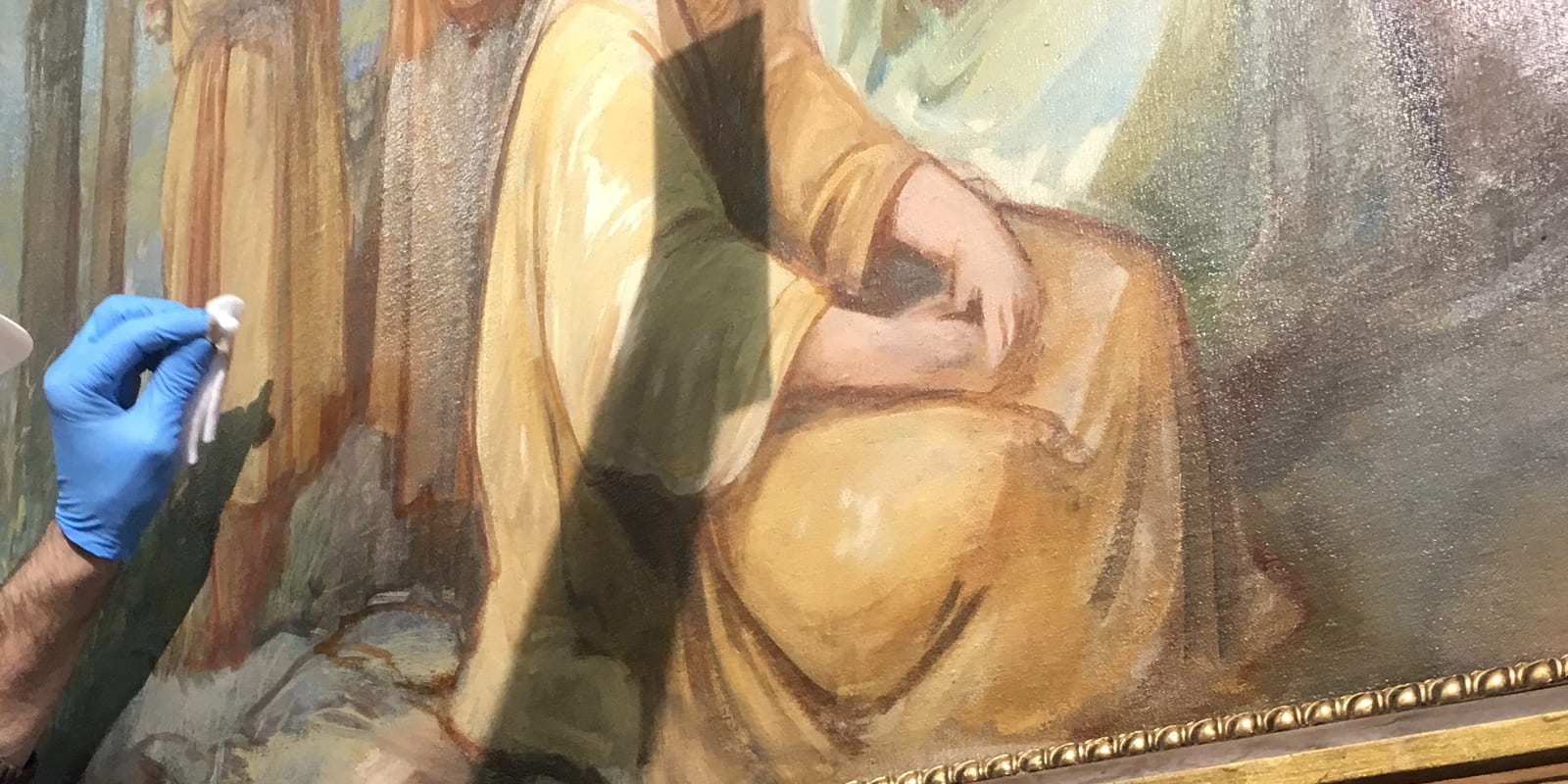
Art has always been a profound reflection of human creativity and culture, capturing moments in time and expressing emotions that transcend generations. However, the passage of time can take its toll on these invaluable creations, leading to deterioration and damage that threaten their integrity and aesthetic appeal. This is where the art of restoration becomes not just a necessity but a crucial endeavor in preserving our artistic heritage.
1. Preventing Further Deterioration
Artworks, whether paintings, sculptures, or textiles, are often made from delicate materials that can degrade over time due to environmental factors such as light, humidity, and pollutants. Without proper restoration, these pieces can continue to deteriorate, potentially reaching irreparable conditions. Restoration aims to stabilize and protect artworks, preventing further damage and ensuring their longevity.
2. Preserving Cultural Heritage
Art embodies the history, values, and traditions of societies throughout the ages. Each piece holds a unique story, offering insights into the past and shaping our understanding of human experience. By restoring artworks, conservators not only safeguard physical artifacts but also preserve cultural narratives for future generations to appreciate and learn from.
3. Retaining Authenticity
Restoration is a meticulous process that requires expertise and sensitivity to maintain the authenticity of an artwork. Skilled conservators use scientific analysis, historical research, and careful techniques to repair damage while respecting the original materials and techniques used by the artist. This ensures that the restored piece remains true to its creator’s vision and historical context.
4. Enhancing Visual Appeal
Art restoration often involves cleaning accumulated dirt, removing discolored varnish, and repairing structural damage such as cracks or tears. These efforts can reveal hidden details, revive vibrant colors, and restore the artwork’s intended visual impact. By enhancing its aesthetic qualities, restoration allows viewers to experience the artwork as it was originally intended, revitalizing its beauty for contemporary audiences.
5. Fostering Education and Appreciation
Restored artworks play a vital role in educational programs and exhibitions, offering opportunities for audiences to engage with cultural history firsthand. Museums, galleries, and educational institutions showcase restored pieces to inspire creativity, provoke thought, and foster a deeper appreciation for art’s enduring significance in society.
6. Ethical Considerations
The ethical practice of art restoration involves balancing intervention with respect for the artwork’s integrity. Conservators adhere to professional standards and principles of minimal intervention, ensuring that their efforts are guided by a commitment to preserving the artist’s original intent and historical value.
In conclusion, the restoration of artworks is not merely about repairing physical damage; it is a commitment to safeguarding our cultural heritage and ensuring that future generations can continue to appreciate the richness and diversity of human creativity. Through meticulous care and expertise, art restoration preserves the past while enriching our present understanding and appreciation of art’s timeless beauty.